API Testing Tutorial
The method of verifying that an API is operating as expected is known as API testing. This API testing tutorial will help you become proficient with the principles.
Introduction to API Testing
Application Programming Interfaces, or APIs, are essential to the modern digital world because they enable communication between various software systems. APIs enable communication between web services and mobile apps, as well as between servers and apps.
In this API testing tutorial, we cover the following concepts:
- Overview of API and API Testing
- API Testing Types
- API Facets
- API Methods
- API Gateway
- Generating Test cases for API testing.
Overview of API and API Testing
Application Programming Interface is what API, an acronym, stands for. A software application’s building blocks, protocols, and routines are called APIs. APIs define the protocol that one software program should use to communicate with other programs.
- Routine: an application that carries out a specific function. Other names for a routine are function, process, and subroutine.
- Protocols: An arrangement for data transfer between two systems.
An API serves as a communication interface that facilitates communication between two software programs.
API Testing
Software testing, known as API testing, is used to verify if an application’s API satisfies requirements for functionality, dependability, performance, and security.
- It can be done both directly on the API and as part of an integration test.
- The primary focus in API testing will be the software architecture’s business logic layer.
- Any software system with several APIs can undergo API testing.
- The application’s appearance and feel won’t be the focus of API testing.
Importance of API Testing
Testing APIs is important for the following reasons:
- By making sure that backend operations move fast and efficiently, well-tested APIs help to create software systems that are more dependable and durable.
- API testing facilitates continuous integration and delivery methods, allowing for quicker and more effective release cycles through test automation and early fault detection.
- It validates the interconnections between various software systems to ensure the application’s basic functionality functions as planned.
- During the development process, early problem discovery can result in significant time and resource savings.
- Extensive testing contributes to the maintenance of data integrity and security, guarding against possible breaches or data losses because APIs frequently handle massive volumes of data and carry out crucial functions.
API Testing Types
API testing entails the following procedures:
Unit Testing: It is the process of testing separate API components separately. It makes sure that every part functions as it should on its own.
Integration Testing: Examining the API’s interactions with other APIs, systems, or services is known as integration testing. It guarantees that the application’s integrated components function as intended.
Regression Testing: It is done to make sure that recent code modifications haven’t negatively impacted the API’s current features. It contributes to preserving stability overall following upgrades or enhancements.
Functional Testing: It evaluates if the API operates and functions as intended. It guarantees that the API maintains its functionality and integrity by providing the appropriate answers for a given request.
Load Testing: Load testing looks at how the API responds to a lot of data and queries. To make sure the API is dependable during periods of high demand, it assesses how well it performs under pressure.
API Documentation Testing: This ensures that the documentation is clear and correct and provides instructions on how to use the API. Comprehensive documentation helps developers use the API correctly.
Security Testing: It verifies that the API is secure and looks for flaws. It assists in locating possible dangers and weak points that malevolent users might try to take advantage of.
Performance Testing: It assesses the API’s stability, speed, and responsiveness. It guarantees that the API functions well in a variety of scenarios and aids in the identification of any performance bottlenecks.
Reliability Testing: Testing for reliability ensures that the API operates well over an extended period of time. It determines whether the API is still dependable and stable even after extended usage.
Validation Testing: This process verifies that the API complies with the requirements and carries out operations as intended. It verifies that the API is using the correct input and output to operate as intended.
Error Handling: This kind of testing looks at the way the API handles exceptions and errors. It ensures that the API provides understandable error messages and that exceptions are managed appropriately to avoid crashes.
Fuzz Testing: Sending erratic or unexpected data to the API and seeing how it responds is known as “fuzz testing.” It strengthens the API’s resilience and assists in identifying weaknesses.
Fault Tolerance Testing: Testing for fault tolerance measures how effectively the API manages unforeseen issues or mistakes. It determines whether the API can function normally even in the face of problems.
Interoperability and WS Compliance testing: WS and interoperability One kind of testing that is relevant to SOAP APIs is compliance testing. By making sure that SOAP APIs comply with the Web Services Interoperability profiles, interoperability between them is verified.
To guarantee that standards like WS-Addressing, WS-Discovery, WS-Federation, WS-Policy, WS-Security, and WS-Trust are appropriately applied and utilized, WS-* conformance is tested.
Advantages of API Testing
Some of the advantages of API testing are:
- Compared to GUI testing, API testing saves time. Less code is needed for API test automation, resulting in faster and better test coverage.
- We can lower the cost of testing by using API testing. Prior to GUI testing, we can identify small flaws with API testing. The GUI testing process will make these small flaws larger. For the company, it will therefore be cost-effective to uncover those flaws during API testing.
- Language is not a factor in API testing.
- When testing core functionality, API testing is quite beneficial. In the absence of a user interface, we can test the APIs. To test the essential features of GUI testing, we must wait until the program is available.
- We can lower the dangers with the aid of API testing.
Use Cases of API Testing
API testing involves sending a request with known data to the API and analyzing the response.
- Data accuracy
- HTTP status codes
- Missing or duplicate functionality
- Response time
- Reliability issues
- Error codes in case API returns any errors
- Authorization checks
- Multithreaded issues
- Error codes if API returns
- Non-functional testing, including security and performance tests.
API Facets
Two main elements are included with APIs:
- Request: A summary of the action taken, together with any relevant information to be forwarded to the server.
- Response: The server sends the client an encapsulation of the data it has processed, along with information about any supplements.
The header is appended to both the request and the response.
API Methods
The operations that can be carried out on the data that an API provides are called API methods, sometimes referred to as HTTP methods. The GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE API methods are the most commonly utilized ones.
GET: Data can be retrieved from a server using this technique. It is simply used to retrieve information; it does not alter any data.
POST: To create a new resource, send data to a server using this method. New data is typically added to the server as a consequence.
PUT: This technique is used to update a server resource that already exists. In order to replace the current data, it transmits data to the server.
DELETE: This command deletes a resource that is currently on the server. It instructs the server to remove the designated information.
These techniques facilitate the execution of diverse actions on the data, thereby simplifying its management and manipulation via APIs.
How are APIs called?
Every UI user interaction has a corresponding API that can be accessed via a URL.
Assuming a user completes a form and hits the “Send” button, the appropriate API will be called upon this event’s trigger.
The image below illustrates how the Request URL points to the “Signup” endpoint.
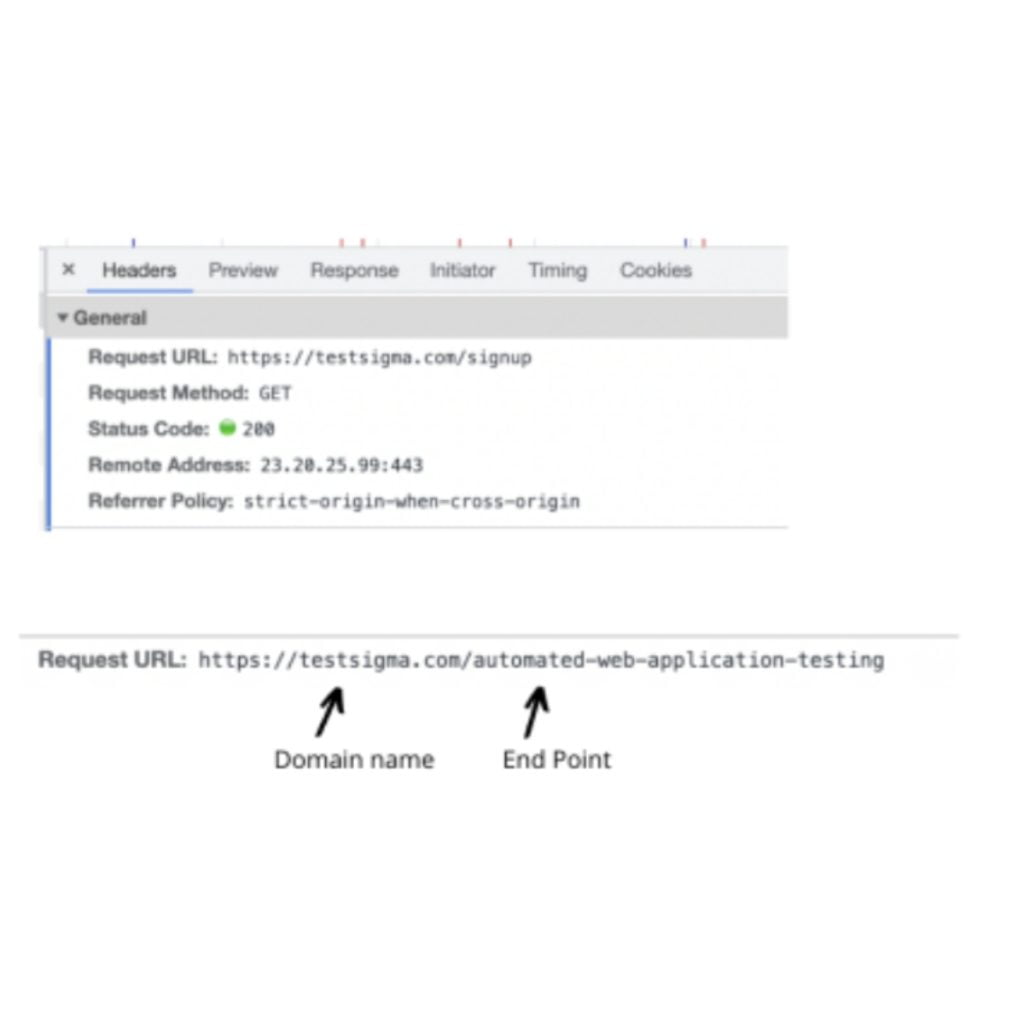
API Gateway
In the real world, using APIs is more complicated. For businesses hosting large-scale APIs, safeguarding them from abuse is their top priority.
Before allowing the calls to proceed with further execution, an API gateway aids in the establishment of authentication.
The functionality of an API gateway extends beyond authentication to include a wide range of services, as follows:
- Routing
- Rate Limiting
- Analytics
- Security
- Policies
API Authentication
Since APIs handle protected resources, request processing needs to be coupled with an authentication mechanism to ensure that access is only authorized for the intended user.
While authorization primarily addresses access management and is activated only when the user has been successfully identified and validated, authentication is the process of confirming the identity of the user.
Basic Authentication
Basic authentication requires the user to verify their identity by entering their username and password.
- Although authentication seems a little flimsy at first, this is how it will operate.
- The user’s credentials are encoded in Base64 when they enter them, creating a key that is then included in the request header and transmitted to the server for validation.
- The server compares the key to the saved password and username.
- The request is fulfilled if the identification is confirmed; if not, an error message is returned, rejecting the request.
API Key Authentication
An application’s long, randomly generated encrypted API key serves as its unique identifier. These are delivered either as a URL or as a component of the request header. The server will handle the request after the client recognizes the API key.
OAUTH Authentication
This method of user authentication is thought to be very strong and safe. Authorization can also be accomplished via the oAuth mechanism.
- To generate a token, a user may first need to check in to the oAuth application using their credentials.
- The request header, which includes the generated token, is submitted to the authentication server for verification.
- The API call will be handled in the event that the token is recognized.
Generating Test cases for API testing
API testing is a type of black box testing in which the implementation of an API is not thoroughly examined.
- It’s also acceptable if you want to specifically go through the code to test the API.
- As with other tests, the primary responsibility while testing an API is to develop the test cases.
Example: REST API
GET https://gorest.co.in/public/v2/users
By examining the API method, we can deduce that it will execute a read operation to obtain the desired details, which include a list of all users.
The format of the response that is returned is JSON. The response body of a REST API is often represented using a JSON structure.
Now let’s begin rotating the test cases for this API.
- The API should return status code 200 (message: Success) upon successful execution.
- By providing the user ID in the URL (https://gorest.co.in/public/v2/users/25) specific user information can be retrieved.
- The JSON response needs to match the schema listed below.
{
“id”:integer,
“name”:string,
“email”:string,
“gender”:string,
“status”:string
}
- An incorrect URL should return 404 (not found).
- The URL with multiple user IDs should return a 404 error.
How to test API
Recognize the Functionality of the API: You must comprehend an API’s functionality before you can begin testing it. This covers the information it shares with the client, the anticipated data format, the input parameters, and the anticipated result.
You may better design your test strategy and make sure your test cases cover all the necessary scenarios by being aware of the capabilities provided by the API.
Verify the API Endpoints: You can start testing the endpoints after you have a firm understanding of the API. This entails using different HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) to submit queries to the API.
Challenges in API testing
The following are a few of the difficulties we encounter when performing API testing:
- Choosing appropriate parameters and combining them
- Clearly classifying the parameters
- Because incorrect call sequencing could result in insufficient testing coverage,
- Validating and confirming the result
- It is very challenging to supply input values because there is no graphical user interface.
Best Practices of API Testing
To guarantee an application’s programming interface’s dependability and usefulness, established practices for API testing are crucial.
- Before beginning the testing process, plan and create the API tests.
- Automate API testing with a testing framework that offers powerful functionality.
- Make test data that encompasses a variety of situations and special cases.
- Check the functionality, security, and performance of the API.
- To make sure that upgrades and modifications don’t affect the functionality of the current API, perform regression testing.
- Connect delivery pipelines and continuous integration with API testing.
- Work together with developers and other interested parties to find and fix problems early.
- Track API performance and find problems before they affect end users by using monitoring tools.
Conclusion
You should feel well-equipped to begin testing your APIs after reading this API testing tutorial, which covers the fundamentals of API testing. Hone your skills by enrolling in our API testing training in Chennai.

